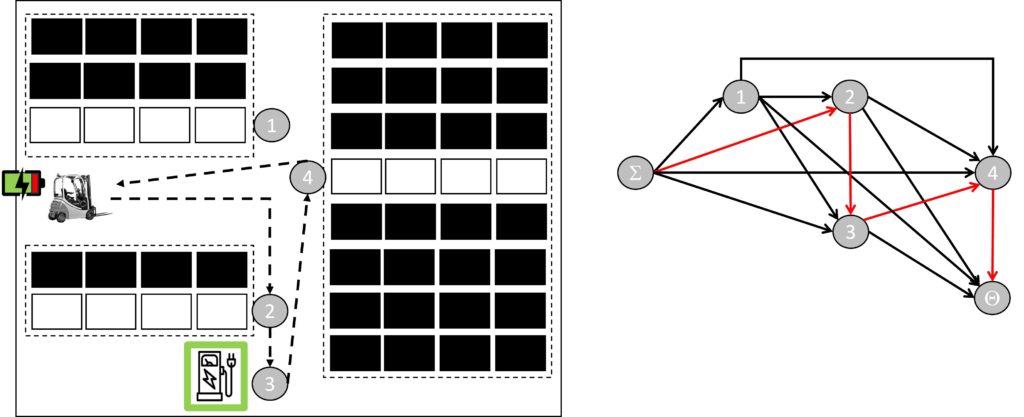
A crucial issue in warehouse management revolves around planning the sequence of operations to perform when items need to be moved within the warehouse, typically using vehicles like forklifts. These operations can involve both storage (moving items form the production area to their designated storage locations) and retrieval (moving items from their storage locations towards the loading docks). The problem addressing this issue is commonly referred to as Sequencing and Routing Problem (SRP).
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainability and environmentally friendly practices in warehouse management, in addition to the traditional focus on operational and economic objectives. This shift has given rise to the concept of the Green SRP (GSRP), which has emerged as a new area of research. Unlike the conventional SRP, GSRP introduces electric vehicles (EVs) alongside traditional vehicles with internal combustion engines, adding complexity to the problem. The challenge in GSRP, in fact, is not limited to planning storage and retrieval operations for both conventional vehicles and EVs. It also includes scheduling break times for EVs to recharge their batteries at available charging stations, considering their limited autonomy.
To address this problem, a mathematical model based on constrained multicommodity flow problems over a structured graph is employed through a mixed-integer linear programming approach. Due to the problem’s complexity, specific resolution methods (various matheuristic approaches), have been developed and tested.
Currently, research is focused on exploring alternative battery management strategies, such as battery swapping, and incorporating smart charging strategies and/or Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) and Vehicle-to-Building (V2B) technologies in this context.
The research is supported by Project PNRR Centro Nazionale 4 “Mobilità sostenibile”, Spoke 10 “Logistica merci” within the activities of the Work Package WP6 – Innovations in Logistic/Multimodal Nodes.
